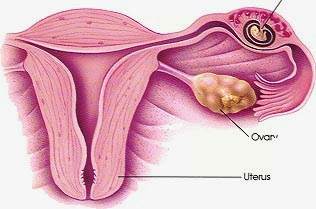
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs and is beyond the normal endometrial, endometrial echogenic thickened, as a result of decidual reaction. Uterine cavity is often filled with fluid exudates produced by the decidual cells on examination is seen as anechoic ring structure, called pseudogestational sac.
Signs and symptoms
1. Signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Signs and symptoms depend on the length of an ectopic pregnancy, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, abortion, or tubal rupture, gestational age at the time, the degree of bleeding that occurs, and the general state of the patient before pregnancy.
1. Pain.
Pain is the main complaint in ruptured ectopic pregnancy. In tubal rupture, lower abdominal pain occurs suddenly and intensity, accompanied by bleeding that causes people to faint and shock occurs. Usually the tubal abortion, pain is not how great and not continuously. The pain initially located on one side; However, after the entry of blood into the abdominal cavity, pain radiating to the middle or to the entire lower abdomen. Blood in the abdominal cavity can stimulate the diaphragm, causing shoulder pain, and when forming retrouterine hematocele, causing painful defecation.
2. Vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is an important sign of both the ruptured ectopic pregnancy, suggesting that it is derived from the fetal death and uterine cavity due to the release of the decidua. Bleeding from the uterus and are usually not a lot of dark brown. Bleeding usually occurs around 51-93% on a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Bleeding means impaired formation of hCG. If there is a solutio placenta decidua can be removed entirely.
3. Amenorrhoea.
Amenorrhoea is the third important sign of ectopic pregnancy, duration of amenorrhea depends on the gestation of the fetus, so it can vary. Most patients do not experience amenorrhea due to fetal death occurred before the next menstruation. Amenorrhea incidence of ectopic pregnancy ranges from 23-97%.
4. On vaginal examination, was found protruding cavity and pain on palpation. Retrouterine hematocele palpable as tumors in douglas cavity, which causes bleeding, and a decrease in blood pressure, increased pulse, and the risk of shock.
Clinical manifestations of ruptured ectopic pregnancy depends on its location. Signs and symptoms vary greatly depending on whether or not the pregnancy ruptured. The symptoms and laboratory test results include:
1. Gastrointestinal complaints.
The most frequent complaints expressed by patients ruptured ectopic pregnancy is pelvic pain. Dorfman stressed the importance of gastrointestinal complaints and vertigo or dizziness. All of these complaints have diversity in terms of incidence due to the speed and extent of bleeding in addition to late diagnosis.
2. Abdominal and pelvic tenderness.
Arising tenderness on palpation of the abdomen and examination, especially by moving the cervix, found in more than three-quarters of cases of ectopic pregnancy or are already experiencing rupture, but it is sometimes not seen before rupture occurrence.
3. Amenorrhea.
History of amenorrhea is not found in a quarter of cases or more. One reason is because patients assume a common vaginal bleeding ectopic pregnancy as a normal menstrual period, thus giving a false date of last menstrual period.
4. Vaginal spotting or bleeding.
During the endocrine functions of the placenta still survive, uterine bleeding usually are not found, but when the endocrine support of the endometrium is no longer sufficient, uterine mucosa will experience bleeding. Bleeding is usually a little, colored dark brown and can be intermittent or persistent.
5. Uterine changes.
Uterus in ectopic pregnancy can be pushed to one side by the ectopic period. In the broad ligament pregnancy or blood filled the broad ligament, the uterus can be shifted great. Uterine cast will be excreted by a minority of patients, perhaps 5% or 10% of patients. Excretion cast fibroids can be accompanied by cramping symptoms similar to networking events abortion spontaneous expulsion of the uterine cavity.
6. Blood pressure and pulse rate.
The initial reaction to the hemorrhage was no change in pulse rate and blood pressure, or sometimes the same reaction as seen in action to be a blood donor phlebotomy is mild increase in blood pressure or vasovagal response accompanied by bradycardia and hypotension.
7. Hypovolemia.
Noticeable drop in blood pressure and pulse rate rise in a sitting position is most often a sign that showed a decrease in blood volume that is quite a lot. All of these changes may have occurred after the onset of serious hypovolemia.
8. Body temperature.
After the acute bleeding, the body temperature may remain normal or even decreased. Higher temperatures rarely found in a state without an infection. Because the heat is a picture that is important to distinguish between who experienced rupture of tubal pregnancy with acute salpingitis, which in this state of body temperatures generally above 38oC.
9. Pelvic mass.
Pelvic mass may be palpable at ± 20 % of patients. The period has the size , consistency and position vary. Usually this mass measuring 5-15 cm , often palpable soft and elastic. However, with the extensive infiltration of the tube wall by the blood of the past can be felt hard. Almost always found in the past pelvic posterior or lateral side of the uterus. Complaints of pain and tenderness often precede palpable in the pelvis future action palpation.
Signs and symptoms
1. Signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
- Early pregnancy symptoms (spots or irregular bleeding, nausea, breast enlargement, discoloration of the vagina and cervix, softening the cervix, uterine enlargement)
- Pain in the abdomen and pelvis.
- Collapse and fatigue.
- The pulse is rapid and weak.
- Hypotension.
- Hypovolemia.
- Acute abdominal pain and pelvic.
- Abdominal distension.
- Rebound tenderness.
- Pale.
Signs and symptoms depend on the length of an ectopic pregnancy, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, abortion, or tubal rupture, gestational age at the time, the degree of bleeding that occurs, and the general state of the patient before pregnancy.
1. Pain.
Pain is the main complaint in ruptured ectopic pregnancy. In tubal rupture, lower abdominal pain occurs suddenly and intensity, accompanied by bleeding that causes people to faint and shock occurs. Usually the tubal abortion, pain is not how great and not continuously. The pain initially located on one side; However, after the entry of blood into the abdominal cavity, pain radiating to the middle or to the entire lower abdomen. Blood in the abdominal cavity can stimulate the diaphragm, causing shoulder pain, and when forming retrouterine hematocele, causing painful defecation.
2. Vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is an important sign of both the ruptured ectopic pregnancy, suggesting that it is derived from the fetal death and uterine cavity due to the release of the decidua. Bleeding from the uterus and are usually not a lot of dark brown. Bleeding usually occurs around 51-93% on a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Bleeding means impaired formation of hCG. If there is a solutio placenta decidua can be removed entirely.
3. Amenorrhoea.
Amenorrhoea is the third important sign of ectopic pregnancy, duration of amenorrhea depends on the gestation of the fetus, so it can vary. Most patients do not experience amenorrhea due to fetal death occurred before the next menstruation. Amenorrhea incidence of ectopic pregnancy ranges from 23-97%.
4. On vaginal examination, was found protruding cavity and pain on palpation. Retrouterine hematocele palpable as tumors in douglas cavity, which causes bleeding, and a decrease in blood pressure, increased pulse, and the risk of shock.
Clinical manifestations of ruptured ectopic pregnancy depends on its location. Signs and symptoms vary greatly depending on whether or not the pregnancy ruptured. The symptoms and laboratory test results include:
1. Gastrointestinal complaints.
The most frequent complaints expressed by patients ruptured ectopic pregnancy is pelvic pain. Dorfman stressed the importance of gastrointestinal complaints and vertigo or dizziness. All of these complaints have diversity in terms of incidence due to the speed and extent of bleeding in addition to late diagnosis.
2. Abdominal and pelvic tenderness.
Arising tenderness on palpation of the abdomen and examination, especially by moving the cervix, found in more than three-quarters of cases of ectopic pregnancy or are already experiencing rupture, but it is sometimes not seen before rupture occurrence.
3. Amenorrhea.
History of amenorrhea is not found in a quarter of cases or more. One reason is because patients assume a common vaginal bleeding ectopic pregnancy as a normal menstrual period, thus giving a false date of last menstrual period.
4. Vaginal spotting or bleeding.
During the endocrine functions of the placenta still survive, uterine bleeding usually are not found, but when the endocrine support of the endometrium is no longer sufficient, uterine mucosa will experience bleeding. Bleeding is usually a little, colored dark brown and can be intermittent or persistent.
5. Uterine changes.
Uterus in ectopic pregnancy can be pushed to one side by the ectopic period. In the broad ligament pregnancy or blood filled the broad ligament, the uterus can be shifted great. Uterine cast will be excreted by a minority of patients, perhaps 5% or 10% of patients. Excretion cast fibroids can be accompanied by cramping symptoms similar to networking events abortion spontaneous expulsion of the uterine cavity.
6. Blood pressure and pulse rate.
The initial reaction to the hemorrhage was no change in pulse rate and blood pressure, or sometimes the same reaction as seen in action to be a blood donor phlebotomy is mild increase in blood pressure or vasovagal response accompanied by bradycardia and hypotension.
7. Hypovolemia.
Noticeable drop in blood pressure and pulse rate rise in a sitting position is most often a sign that showed a decrease in blood volume that is quite a lot. All of these changes may have occurred after the onset of serious hypovolemia.
8. Body temperature.
After the acute bleeding, the body temperature may remain normal or even decreased. Higher temperatures rarely found in a state without an infection. Because the heat is a picture that is important to distinguish between who experienced rupture of tubal pregnancy with acute salpingitis, which in this state of body temperatures generally above 38oC.
9. Pelvic mass.
Pelvic mass may be palpable at ± 20 % of patients. The period has the size , consistency and position vary. Usually this mass measuring 5-15 cm , often palpable soft and elastic. However, with the extensive infiltration of the tube wall by the blood of the past can be felt hard. Almost always found in the past pelvic posterior or lateral side of the uterus. Complaints of pain and tenderness often precede palpable in the pelvis future action palpation.
Komentar
Posting Komentar